简介
SkipList(跳表)这种数据结构是由William Pugh于1990年在在 Communications of the ACM June 1990, 33(6) 668-676 发表了Skip lists: a probabilistic alternative to balanced trees,在其中详细描述了他的工作。由论文标题可知,SkipList的设计初衷是作为替换平衡树的一种选择。
我们都知道,AVL树有着严格的O(logN)的查询效率,但是由于插入过程中可能需要多次旋转,导致插入效率较低,因而才有了在工程界更加实用的红黑树。
但是红黑树有一个问题就是在并发环境下使用不方便,比如需要更新数据时,Skip需要更新的部分比较少,锁的东西也更少,而红黑树有个平衡的过程,在这个过程中会涉及到较多的节点,需要锁住更多的节点,从而降低了并发性能。
SkipList还有一个优势就是实现简单,SkipList的实现只花了2个小时,而红黑树,我可能得2天。
时隔将近三十多年,SkipList这种数据结构仍在许多途径有用武之地,比如Redis, 还有Google的著名项目Bigtable.
原理及实现
其实跳表就是在普通单向链表的基础上增加了一些索引,而且这些索引是分层的,从而可以快速地查的到数据。如下是一个典型的跳表:
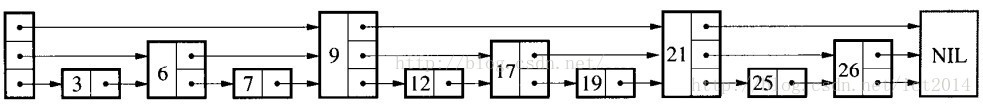
###查找
查找示意图如下:
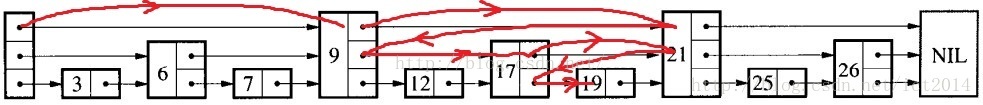
比如我们要查找key为19的结点,那么我们不需要逐个遍历,而是按照如下步骤:
- 从header出发,从高到低的level进行查找,先索引到9这个结点,发现9 < 19,继续查找(然后在level==2这层),查找到21这个节点,由于21 > 19, 所以结点不往前走,而是level由2降低到1
- 然后索引到17这个节点,由于17 < 19, 所以继续往后,索引到21这个结点,发现21>19, 所以level由1降低到0
- 在结点17上,level==0索引到19,查找完毕。
- 如果在level==0这层没有查找到,那么说明不存在key为19的节点,查找失败
既然算法都有了,实现也不在话下,如下是C++实现:
|
|
插入
如下是插入结点示意图:
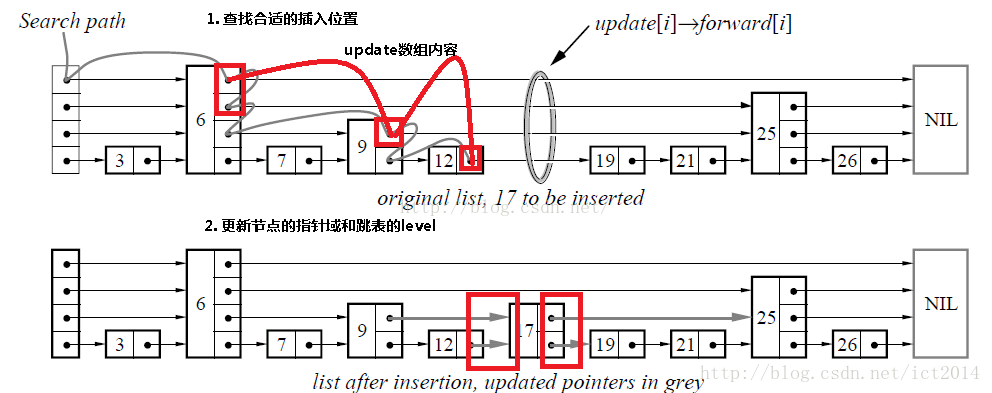
其实插入节点的关键就是找到合适的插入位置,即从所有小于待插入节点key值的节点中,找出最大的那个,所以插入节点的过程如下:
- 查找合适的插入位置,比如上图中要插入key为17的结点,就需要一路查找到12,由于12 < 17,而12的下一个结点19 > 17,因而满足条件
- 创建新结点,并且产生一个在1~MAX_LEVEL之间的随机level值作为该结点的level
- 调整指针指向
插入的代码如下:
|
|
移除
移除结点的示意图如下:
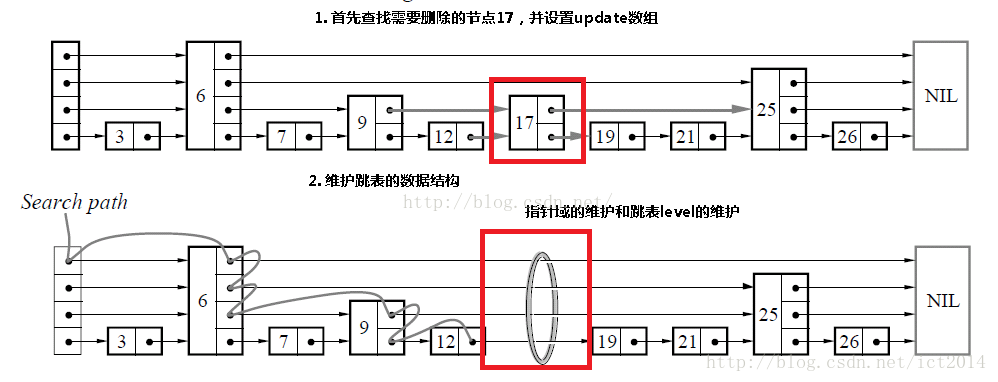
移除结点其实很简单,就分以下3步:
- 查找到指定的结点,如果没找到则返回
- 调整指针指向
- 释放结点空间
代码如下:
|
|
完整代码
已经把代码放到github上,地址为 https://github.com/HiWong/SkipListPro